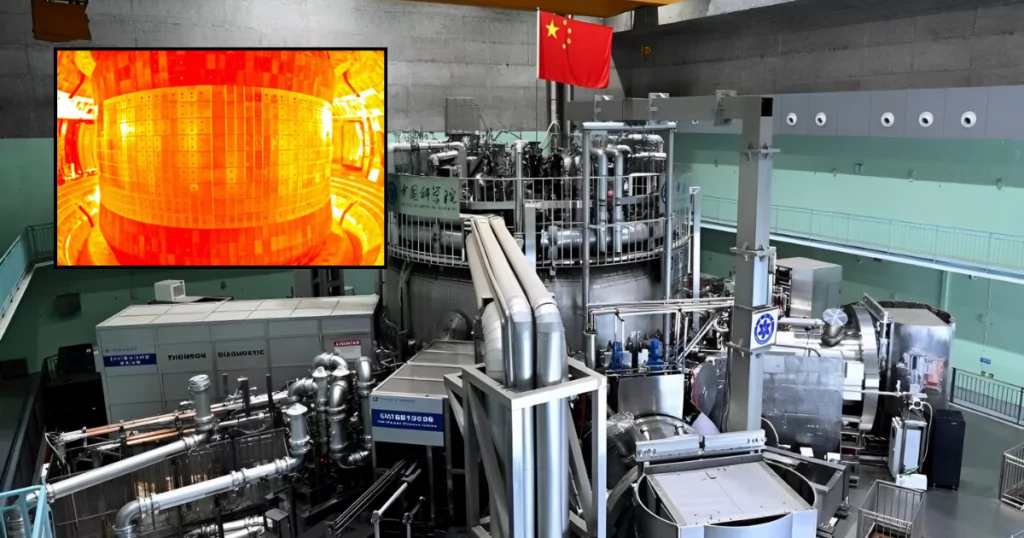
In an awe-inspiring display of technological prowess, China has once again cemented its position at the forefront of innovation. The country’s Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), commonly referred to as the “artificial sun,” sustained a record-breaking temperature of 100,000,000 degrees Celsius for 1,056 seconds (17 minutes and 36 seconds). This achievement represents a monumental step toward creating a sustainable and limitless energy source through nuclear fusion.

What Is the Artificial Sun?
The artificial sun is an advanced nuclear fusion reactor designed to replicate the energy-producing process of the sun. Unlike nuclear fission, which splits atoms to release energy, nuclear fusion fuses hydrogen atoms to create helium, generating immense energy in the process. Fusion is considered the “holy grail” of energy production because it produces no greenhouse gases and leaves behind no long-lived radioactive waste.
China’s EAST is a part of the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) initiative, a global collaboration involving 35 countries, including the United States, Russia, and members of the European Union. However, China’s recent success with EAST sets it apart, showcasing its ability to independently achieve results on a scale that rivals international efforts.
Breaking the Records
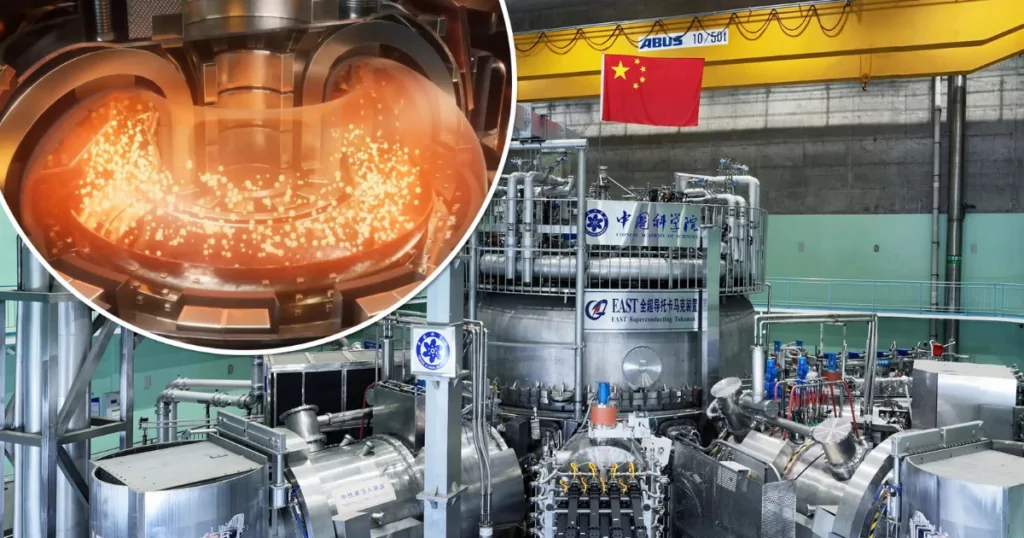

Previously, China set the record by sustaining plasma at 120 million degrees Celsius for 101 seconds. This latest experiment shattered that record by maintaining 100 million degrees for over 1,000 seconds. To put this into perspective, the sun’s core temperature is approximately 15 million degrees Celsius. This means China’s artificial sun achieved a temperature more than 6 times hotter than the sun’s core and sustained it for an unprecedented length of time.
The director of the project, Gong Xianzu, described the achievement as a critical step toward the ultimate goal of producing stable, clean, and nearly infinite energy.
Why Is This Significant?
The success of China’s artificial sun represents a turning point in the quest for sustainable energy solutions. While renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power are crucial for combating climate change, nuclear fusion could provide a more reliable and virtually inexhaustible source of energy. By replicating the process that powers the stars, humanity could finally unlock a solution to the growing global energy crisis.
Fusion energy holds several advantages:
- Sustainability: The fuel used for nuclear fusion, hydrogen isotopes, is abundant and can be extracted from seawater.
- Safety: Unlike nuclear fission, there is no risk of a meltdown, and the byproducts are not long-lived or highly radioactive.
- Efficiency: A small amount of fusion fuel can produce massive amounts of energy, significantly surpassing the efficiency of traditional energy sources.
Challenges on the Road to Fusion Power
Despite this groundbreaking achievement, nuclear fusion is not without its challenges. Sustaining plasma at extreme temperatures for a significant amount of time requires advanced materials and precise magnetic confinement. EAST uses superconducting magnets to create a powerful magnetic field, which keeps the plasma stable and prevents it from touching the walls of the reactor.
Additionally, the high cost of constructing and maintaining fusion reactors poses a significant barrier to widespread adoption. China’s EAST, for example, has required billions of dollars in investment since its construction began in 2006. However, the potential long-term benefits far outweigh the initial costs.
Implications for the Future
The success of China’s artificial sun could have far-reaching implications for the global energy landscape. By demonstrating the feasibility of sustained nuclear fusion, China has paved the way for future advancements that could eventually lead to commercial fusion reactors. Such reactors could revolutionize industries, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and contribute to global efforts to combat climate change.
The project also underscores China’s commitment to becoming a global leader in science and technology. With significant investments in research and development, China continues to push the boundaries of what is possible, setting new standards for innovation and collaboration.
Global Collaboration and Competition
While China’s achievement is remarkable, it is important to recognize the collaborative nature of nuclear fusion research. The ITER project, based in France, is one of the most ambitious energy projects in history and involves scientists and engineers from around the world. China’s progress with EAST complements the efforts of ITER and other international initiatives, highlighting the importance of shared knowledge and expertise in tackling global challenges.
At the same time, the success of EAST demonstrates China’s growing dominance in the field of clean energy technology. As the world grapples with the effects of climate change, countries that lead in the development of sustainable energy solutions will play a crucial role in shaping the future.
Conclusion
China’s achievement with the artificial sun is a testament to human ingenuity and perseverance. By sustaining a temperature of 100 million degrees Celsius for 17 minutes, scientists have moved one step closer to unlocking the potential of nuclear fusion as a viable energy source. While challenges remain, this breakthrough offers hope for a future powered by clean, limitless, and sustainable energy.
As global efforts to combat climate change intensify, innovations like China’s artificial sun will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping a brighter and more sustainable future.


